Thermography in the Metall Industry
In the metal industry, the continuous improvement of process reliability and productivity has the highest priority. Above all, metal products should be of high quality and durable as well as cost-efficient and resource-efficient to produce.
Thermography can support the achievement of these goals. In this context, thermographic systems take on different tasks at different points in the complex processes of metal processing:
Monitoring of temperatures, for example during casting, melting, forming
Analysis of material properties in stress tests, as part of quality assurance
Detection of weak points or processing defects, for example on weld seams
Safety-relevant monitoring, for example of melting furnaces and casting ladles
Areas of Application for Thermography in the Metal Industry
Products made of metal materials are needed for numerous applications in the manufacturing industry, including the automotive industry, machine and plant construction and the transport sector. The requirements in the various areas of the metalworking industry are very different.
In most metal processing methods, the temperature and its distribution play a decisive role. Even minimal deviations from the target temperature can, for example, negatively influence the predefined strength properties of the product. This, in turn, leads to high reject rates and costs. Infrared camera-supported process monitoring makes this scenario avoidable. Thermographic systems operating in the short-wave infrared range (SWIR) are particularly suitable for non-contact temperature measurement on metallic surfaces.
For the detection of slag formation during tapping and the monitoring of ladles and furnaces, however, infrared cameras that measure in the long-wave infrared range are often an advantage.
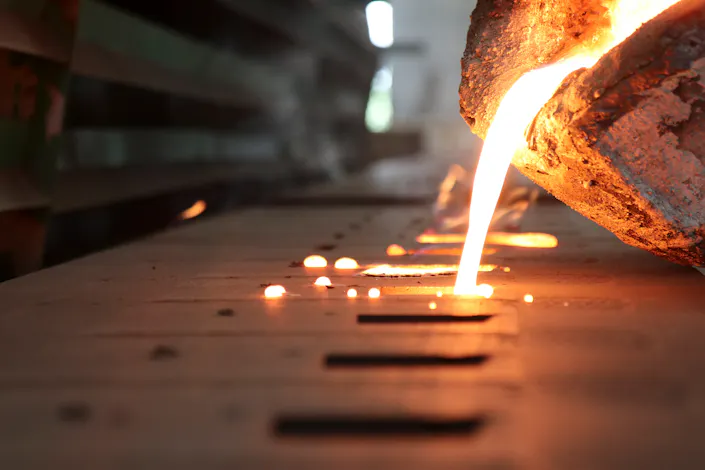
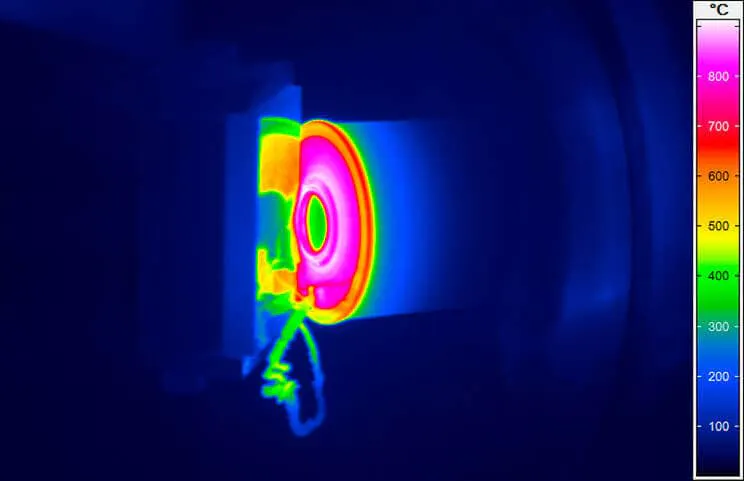
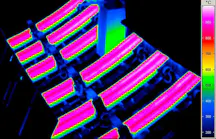
Casting - Quality Assurance During Production
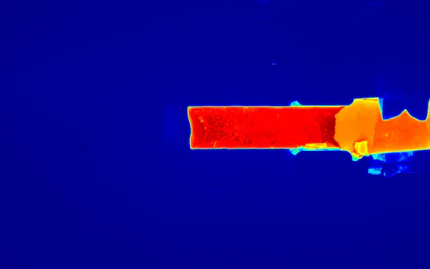
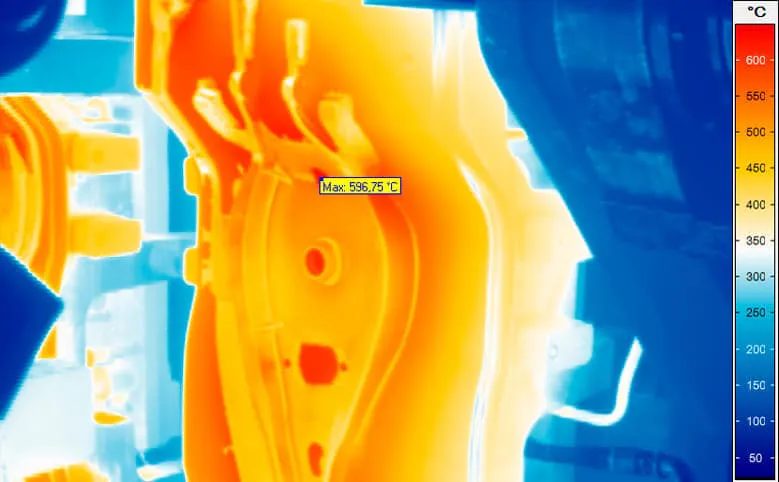
A central and decisive factor in the entire casting process is the temperature, which determines the properties and thus the quality of the end product. This already begins with maintaining the material-specific melting temperature to achieve the optimum consistency of the molten metal. In addition to the melt treatment, the temperature also influences the solidification of the melt and the resulting microstructure, which in turn determines the hardness and strength of the finished casting.
Benefits of Thermography for Casting
Monitoring mould and melting temperature
Optimising energy input
Ensuring quality of the casting (strength, stability, no cavities)
Ensuring safety for people and the environment
By determining the temperature once, by means of a contact measurement before the start of the casting process, process control is possible on the basis of existing experience regarding cooling behaviour. However, this reaches its limits when casting speed and/or duration are subject to stronger fluctuations. To ensure that the required minimum temperature of the molten metal is maintained up to the end of the process in these cases as well, non-contact temperature measurement by means of thermography is a reliable method. In addition, an optimisation of the energy input can be achieved by reducing the temperature reserve that has to be maintained.

A challenge in terms of measurement technology is the influence of the emissivity in molten metals. Their surfaces are highly reflective in the medium and long-wave spectral range and the emissivity has an even lower value than in the solidified state. Any deviation in the surface condition can affect the temperature reading.
By using thermographic systems that measure in SWIR spectral range, such interference effects can be suppressed. Infrared cameras make a significant contribution in this respect, as they can measure melting temperatures without contact. Even the smallest temperature deviations, which would have a considerable impact on the flowability and quality of the melt, can be directly detected and quickly corrected.
The temperature of the moulds is just as decisive. In order to avoid the formation of blowholes due to gas in the casting, the mould temperature can be permanently tested with the help of thermographic systems and readjusted if necessary.
Finally, non-contact temperature measurement also plays a significant role in the heat treatment of metal workpieces. With this method, the mechanical properties of the corresponding metal products are to be improved. This requires controlled heating and cooling for the targeted modification of material properties, which can be elegantly monitored with thermographic systems.
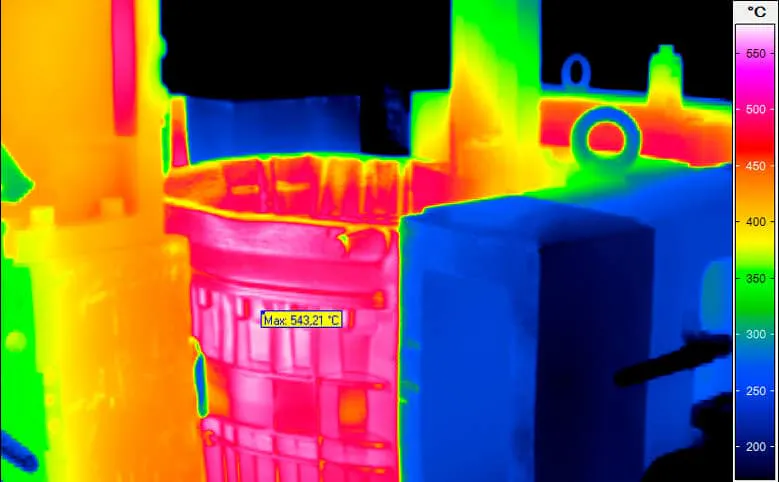
More Safety in the Foundry Industry
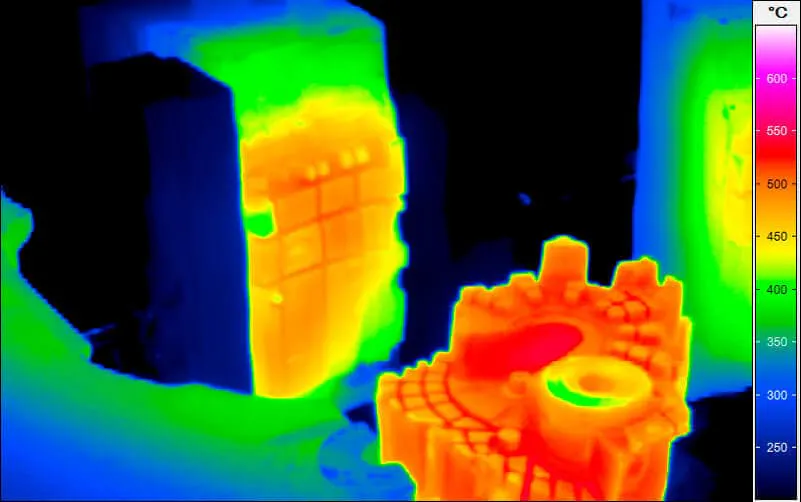
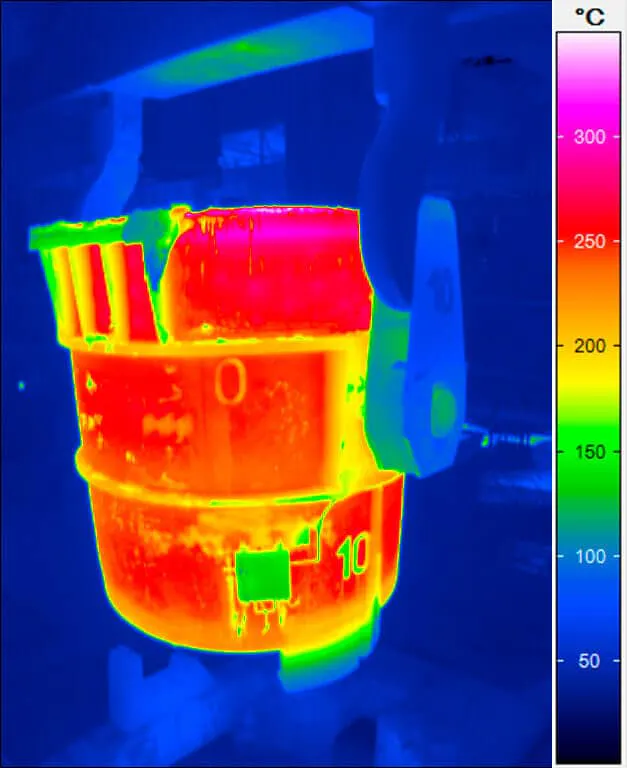
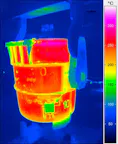
Casting moulds (especially permanent moulds) as well as melting furnaces and casting ladles are subject to technologically induced wear during their use. To ensure that the safety of people and the environment can be always guaranteed, thermographic monitoring is also useful here. Infrared cameras in the long-wave infrared range (LWIR) can be used, for example, to reliably identify leaks and cracks in moulds and furnaces or scouring on refractory linings and to derive safety measures from them. The targeted repair of the defects reduces the energy required in the process and avoids high costs that would be associated with a production stoppage. At the same time, serious accidents such as the leakage of melt from broken ladles can be prevented.
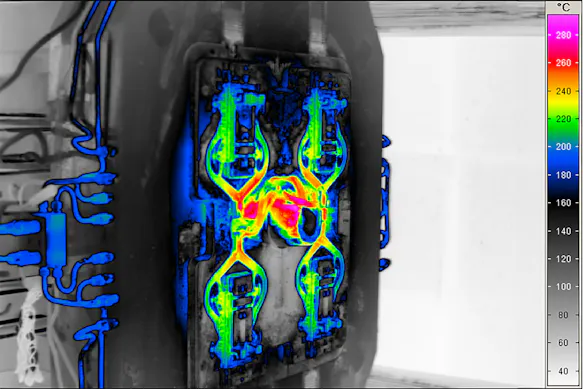
Thermal Images from Casting Processes
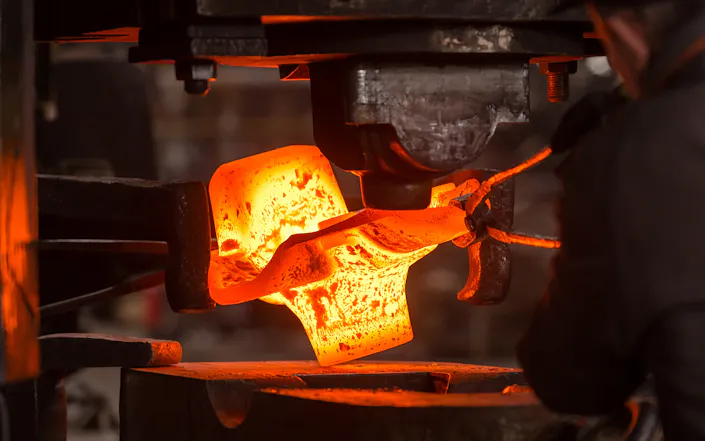
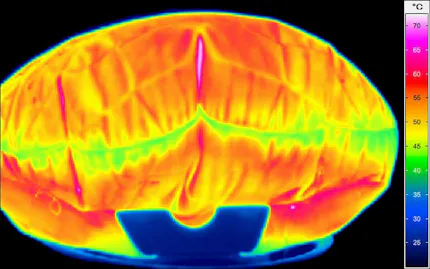
Thermography in Hot Forming
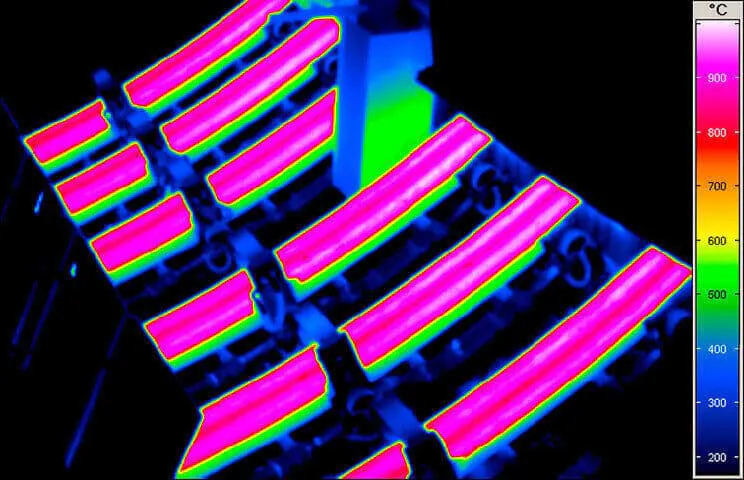
Hot forming is a process of great importance for many industries such as vehicle manufacturing and the construction industry as well as their suppliers, as the parts produced in this way are very light and yet extremely stable. To ensure consistently high manufacturing quality in this process, all production steps are subject to strict quality monitoring.
All hot forming processes are performed above the recrystallisation temperature of a metal. This allows high degrees of forming with low forming forces at the same time.
Benefits of Thermography for Hot Forming Processes
Ensuring the quality in all production steps
Monitoring temperatures and detecting deviations quickly
Optimising energy input
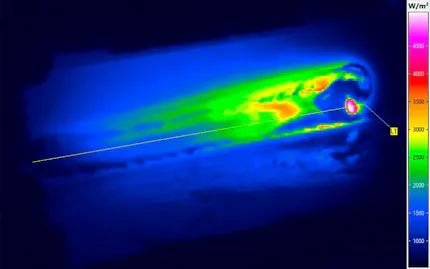
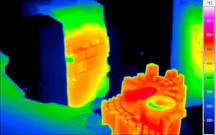
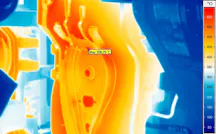
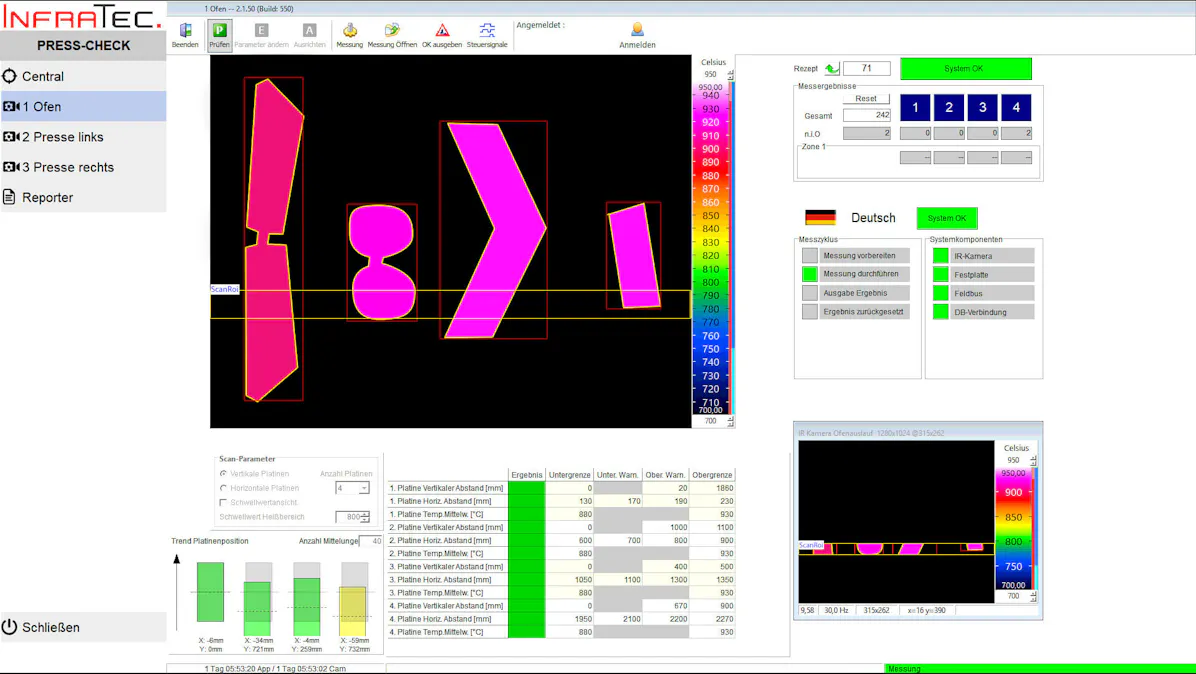
The most modern process variants of press hardening also work with controllable tool cooling, through which different cooling rates and thus different degrees of hardness can be achieved within one and the same workpiece. Continuous thermographic monitoring allows both control of the process conditions during each individual pressing process and early detection of incipient systematic deviations.

Thermography in Use in Press Hardening
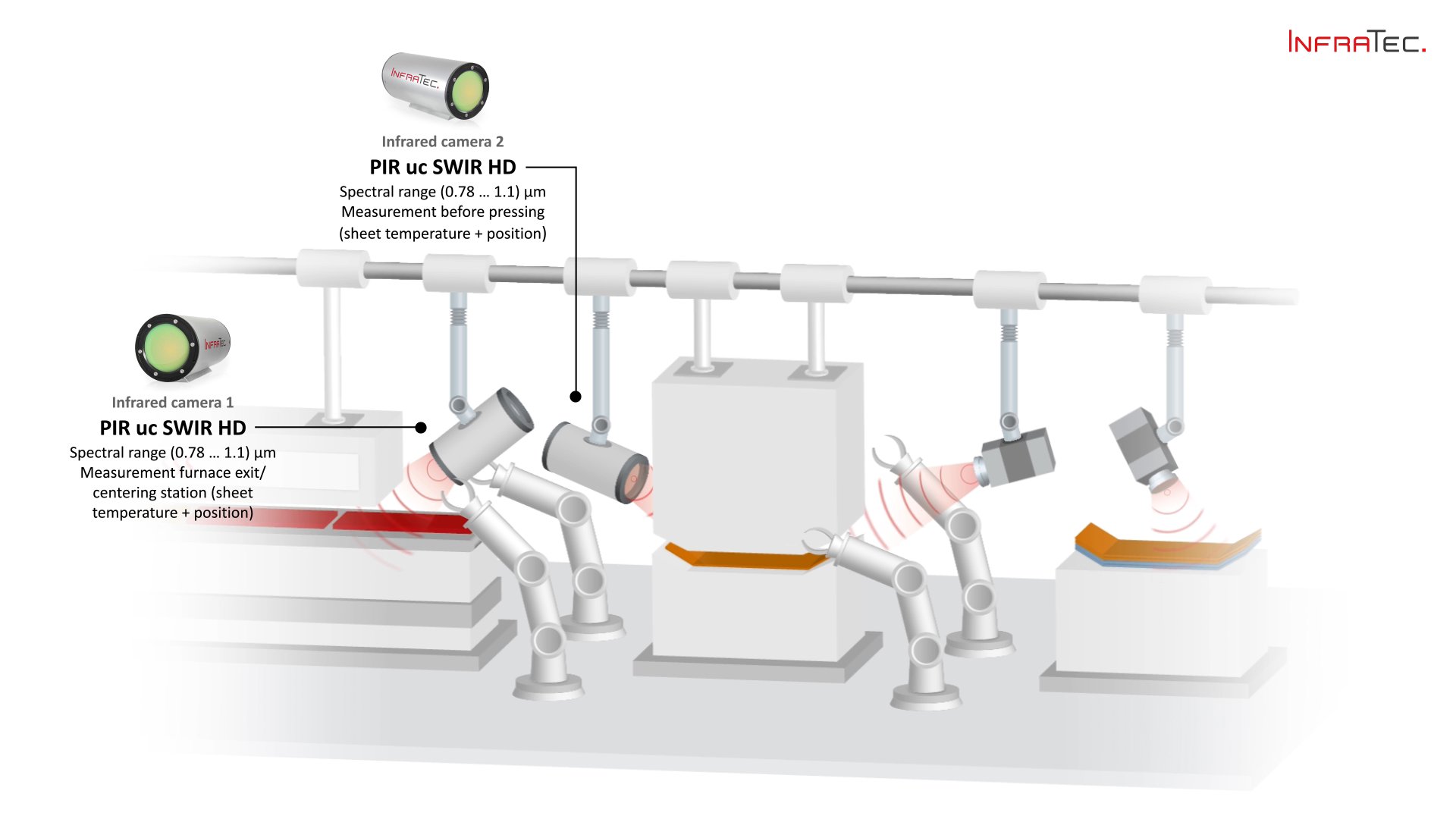
To make the heating processes as efficient as possible and to save energy, thermographic systems detect without contact when the optimum forming temperature of the workpiece has been reached. Both the homogeneity of the temperature distribution and compliance with the target temperature are measured. With a view to energy efficiency, this means that only the energy is introduced, which is necessary for the forming process.
Tip!
Even if the starting material for this process is precisely specified in terms of its pressing properties, its thermographically relevant surface properties are a variable parameter. Using infrared cameras in the SWIR spectral range, however, it is possible to reduce measurement errors caused by emissivity.
Thermal Images from Hot Forming Processes
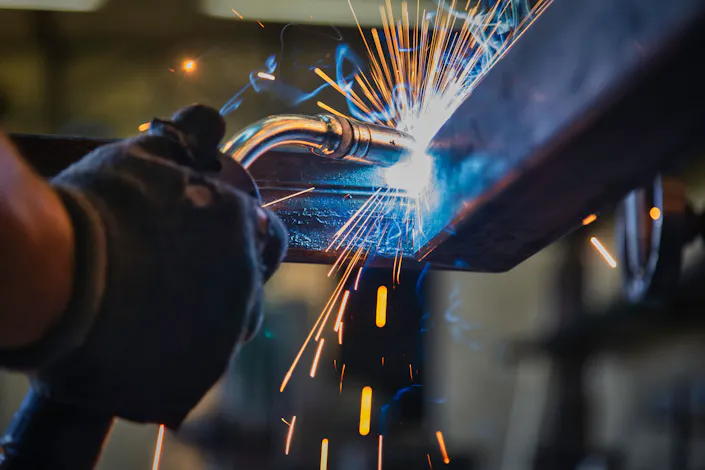
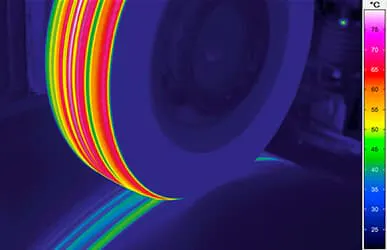
Thermography in Welding
The purpose of welding is to permanently substance-to-substance bond two workpieces by applying pressure and/or heat so that they meet the specified quality criteria. Thermography is an established method for monitoring compliance with specified temperatures during the welding process or for non-destructive analysis of welded joints that have already been produced.
The way in which two joining partners are welded together depends on the respective welding process. While in laser welding, for example, the material of the joining partners is melted with a laser to join them together, in resistance welding current is induced to generate heat in order to heat the joining partners up to the welding temperature and then to join them together under the effect of great force.
Benefits of Thermography for Welding
Monitoring temperature development and distribution and quickly detecting deviations
Optimising energy input
Detecting and avoiding defects such as cavities, cracks, and bonding defects
Ensuring the quality of the weld seams
Ensuring the quality of the end products
Whichever process is used, temperature adjustment and control are essential in all heat-based welding processes to achieve high quality results.
This is where infrared cameras are applied. They are used to monitor compliance with the process temperatures and their development over time during the entire welding process. In most cases, the temperature distribution on the surfaces of the joining partners, the detection of thermal anomalies and the measurement of the melt or liquidus temperatures are relevant. Thermography is also used in the final quality assurance process when components are inspected for defects such as cracks, cavities, and bonding defects with regard to their stability. In this particular case, active thermography is used, in which energy is introduced into the component with the help of external excitation sources, e.g., lasers, inductors or flash lamps. This in turn leads to local temperature differences on the surface over time, if there are defects inside.

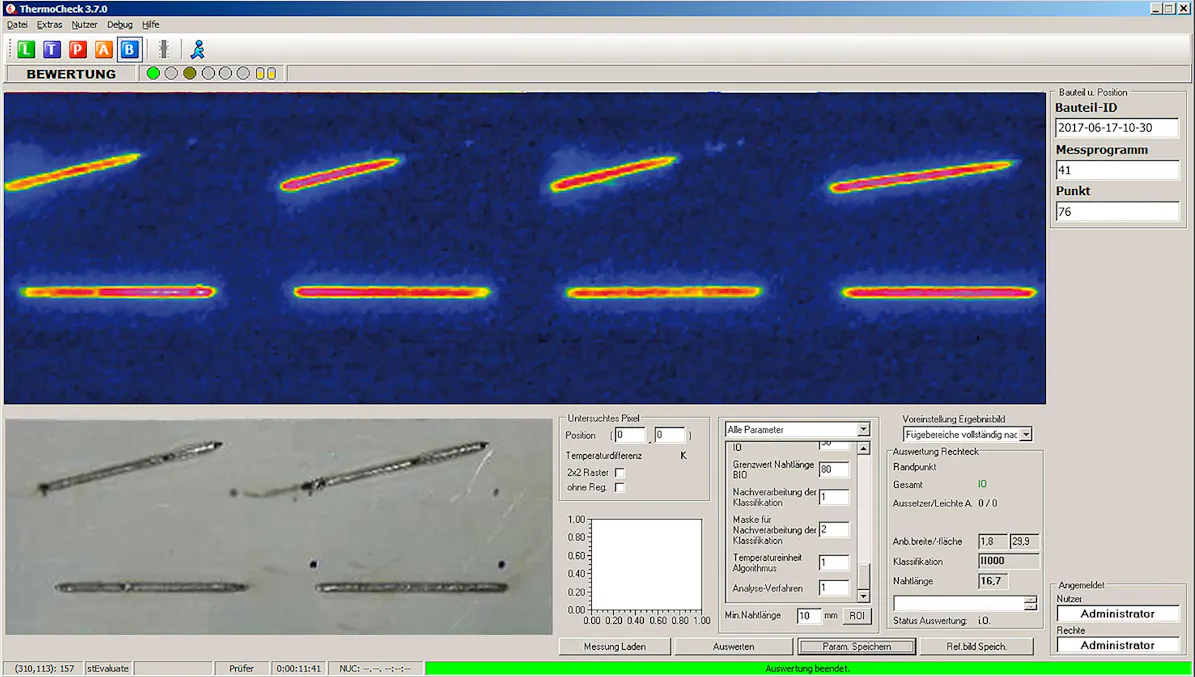
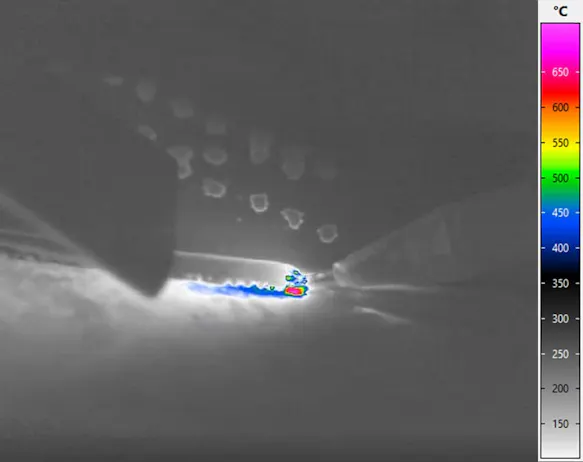
Thermography in Soldering
Other than welding, soldering is a joining process in which metals are joined together by melting solder. The components to be joined are not melted or fused. One challenge is to bring the joining partners up to the working temperature of the solder to avoid cracks.
Furthermore, during soldering, porous tear-off areas and pores which may result from the overheating of the solder or the flux during the soldering process should be avoided. As with the welding processes, it is also recommended to always monitor the process temperature during the soldering process and to control it accordingly.
Benefits of Thermography for Soldering
Monitoring temperature development and distribution and quickly detecting deviations
Optimising energy input
Ensuring the quality of the end products
Tip!
The SWIR range in particular offers good conditions for temperature measurement with significantly reduced emissivity influence. In addition, lenses with a very small field angle are available that allow a safe distance between the camera and the welding point and are also characterised by an extremely small design.

Which System Solution is Suitable for Which Application?
While non-metallic objects typically have a high and less variable emissivity, the opposite is true for metals. Here, the variable emissivity becomes a significant factor influencing measurement accuracy. For this reason, SWIR thermography systems are recommended for measurements on metal surfaces. The reason for this is a physical law: the shorter the wavelength in which a thermographic camera operates, the more dynamically the intensity of the infrared radiation it detects rises or falls with a change in the temperature of the object being measured. In turn, the influence of possible deviations in the surface characteristics of the object, which would otherwise lead to considerable falsification of the measured values, decreases. SWIR infrared cameras enable the reliable measurement of temperatures from 300 °C and are thus predestined for use in metal processing. In the area of safety monitoring on casting ladles, melting furnaces, etc., LWIR thermography systems are preferably used, as the temperatures here are mostly below 300 °C and the emissivity is higher and thus less variable, which significantly simplifies the measurement.
What is Emissivity?
The emissivity is the measure of the ability of an object to emit infrared radiation. The black body as a radiation-physical model has the highest possible emissivity with the value 1 (= 100 %), which is also independent of the wavelength.
The emissivity of real measurement objects, on the other hand, can depend on the wavelength and is primarily influenced by the following parameters:
Material composition (surface)
Surface roughness
Viewing angle to the surface normal
Object temperature

Would You Like to Know More?
It is not unusual for tasks to be associated with special requirements. Discuss your specific application needs with our specialists, receive further technical information or learn more about our additional services.