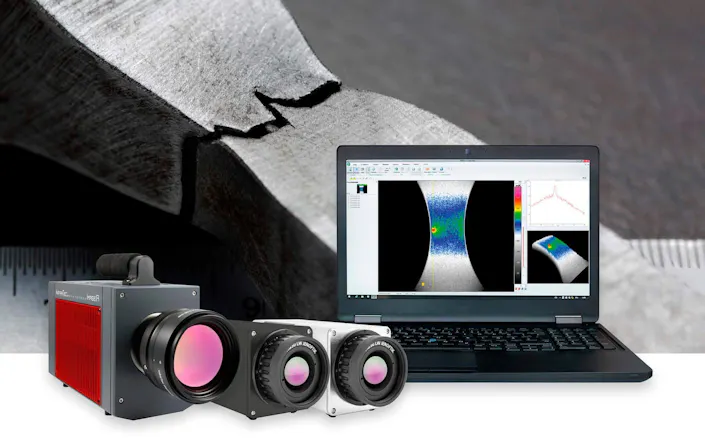
Thermography for Material Testing
Efficient non-destructive testing of a wide variety of materials and defect types
Non-destructive testing saves time and costs
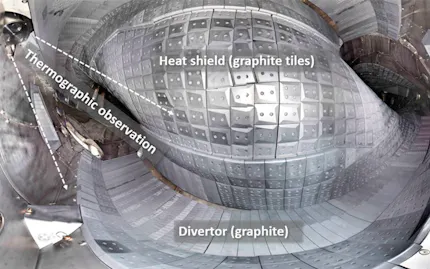
Analysis of process immanent temperature differences or externally induced heat streams
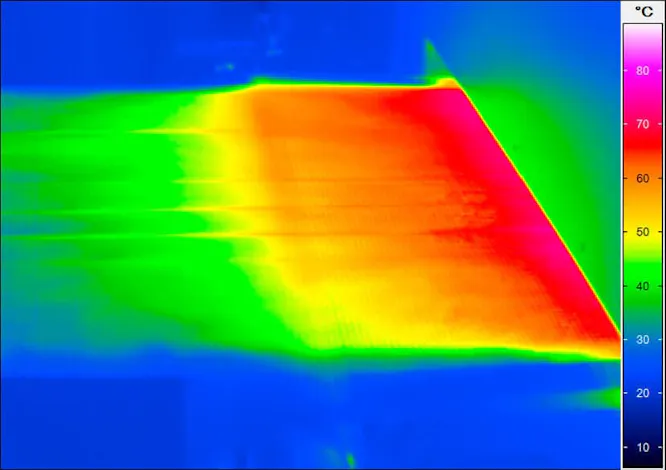
Pulsed activation allows the detection of below-surface errors
In-line applications for permanent quality control possible
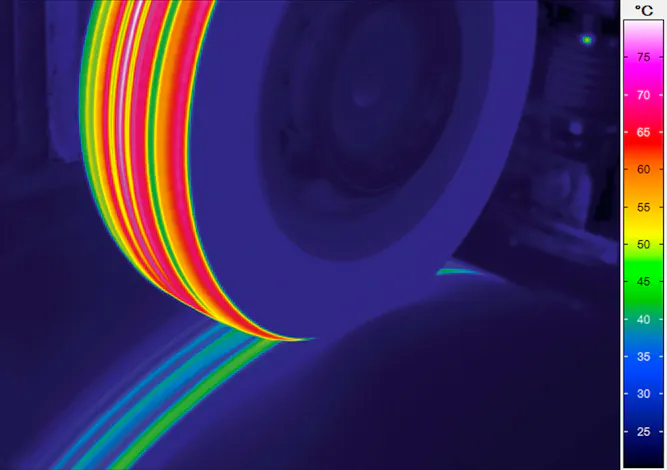
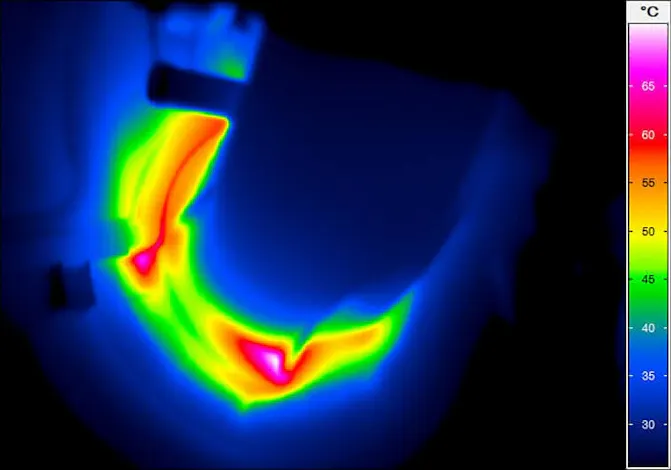
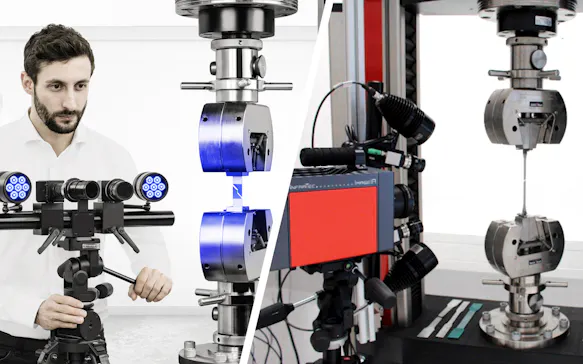
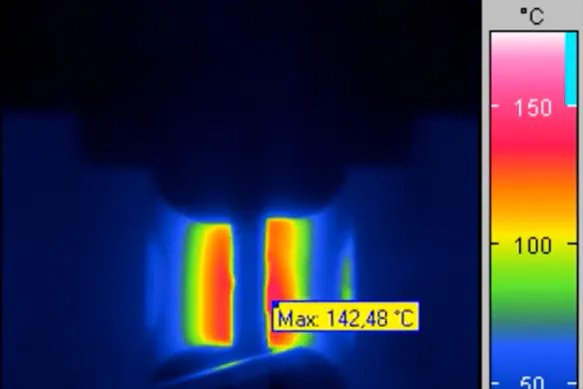
Sensitive heat measurements to indicate areas of different mechanical stress
Infrared Camera Systems Minimise Product Waste from Testing Procedures
Material tests using thermal imaging save time and costs as test objects will not be destroyed during process. They can be used for further testing or locating quality problems that could be corrected. NDT tests with infrared camera systems provide good solutions with greater applications as they can be used for a wide range of different materials and types of defects. A huge advantage is that thermographic testing procedures can be applied to larger areas at once in comparison to ultrasonic or other methods that focus on smaller zones.
Thermography can be used for:
Live Online Events 2026
Passive Thermography as well as Active Heat Flow Thermography Locates Defects
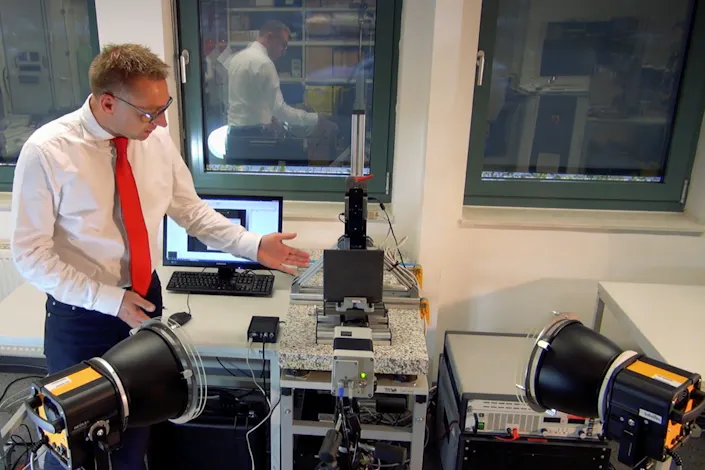
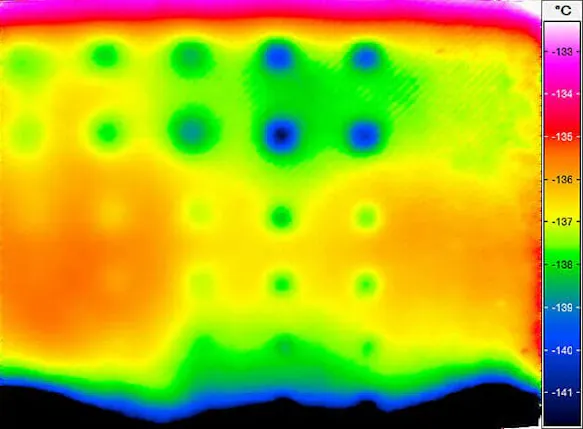
Which method of thermography is used for material testing depends decisively on the question of the origin of the heating of the test object. In one test mode, it could stem directly from heating the test object gains during its production process. This case is referred to as passive thermography. The other possibility is called active heat flow thermography or just active thermography. This is when the test object will be thermally activated by an external energy input for instance by a halogen radiator or a flash lamp.
Online Events On Demand
Efficient Material Testing – Non-destructive and Contactless
Theoretical background – mechanical force, stress and temperature Methods for analysis
Examples from practice with application samples – elastic periodical load test and fatigue test
Short overview about InfraTec products
Complementary technical lecture
"Contribution of Thermoelastic Stress Analysis in mechanics of materials and structures: some illustrations" from Prof. Vincent Le Saux, École Nationale Supérieure de Techniques Avancées Bretagne

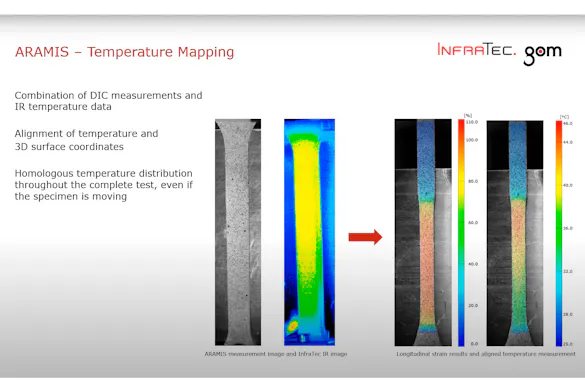
Thermography and Digital Image Correlation – A Winning Team in the Materials and Components Testing Field.
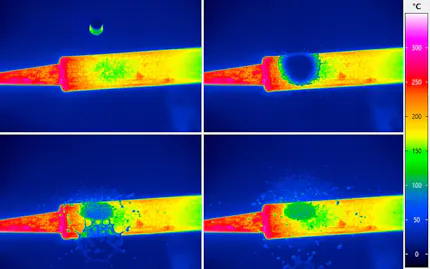
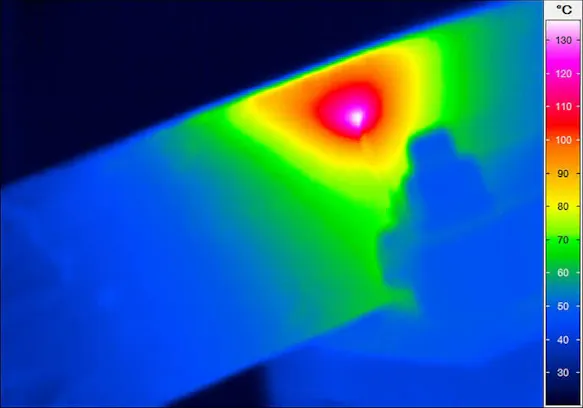
Active thermography for non-destructive testing
Synchronizing high-tech sensors: ZEISS/GOM ARAMIS and infrared cameras from InfraTec
Tracking of temperature on homologous points in 3D space
Applications in materials, components and electronic testing
Complementary technical lecture "The IGI EcoMapper – High-Precision Aerial Survey in Five Spectral" from Dr. rer. nat. Jens Kremer, Manager R&D, IGI mbH, Germany
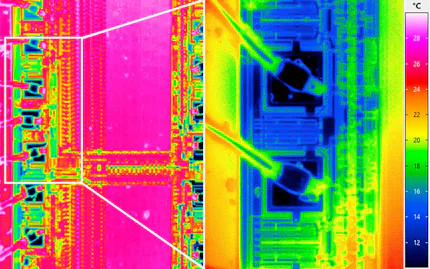
Infrared Lock-in Thermography for Inspection of Electronics and Integrated Circuits
Failure analysis and defect inspection, quality and process control and flexible R&D solution
Hotspot detection on printed circuit boards, integrated circuits, semiconductor material and multi-chip modules
Detection of faulty thermal connections of heat sinks, short circuits, soldering defects and wire bonding errors
Complementary technical lecture Semiconductor IR-LIT Analytics – Challenges and Case Studies from Marko Hoffmann; Infineon Technologies Dresden GmbH & Co. KG

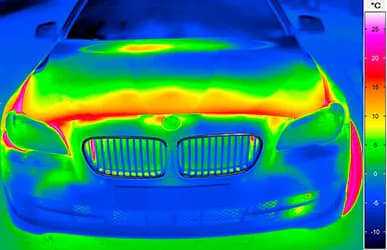
Applications for Thermal Imaging on Wind Power Systems
General information about infrared thermography and presentation of different infrared camera techniques
Monitoring wind turbine power plants by (passive) thermography
Principle & methods of active thermography and examples
Technical Lecture “Inspection of Wind Turbine Blades with Ground-based Passive Thermography” from Michael Stamm, Federal Institute for Materials Research and Testing (BAM)


Would You Like to Know More?
It is not unusual for tasks to be associated with special requirements. Discuss your specific application needs with our specialists, receive further technical information or learn more about our additional services.
Lock-In Thermography is Integrated in IRBIS® 3 Software
Active thermography can detect defects even more precisely when the activation of the test object will be carried out in a pulsed mode. Thereby it will be possible to detect faults which are located in deeper subsurface layers. Such analysis algorithms like the one of lock-in thermography are already available as a module of the IRBIS® 3 software family. The adaptation to the specific application can be done quite easily with flexibility. InfraTec can also provide customer specific and complete active thermography test solutions.